SET : 1
1. 1. Derive the design equation for a batch reactor. Write the advantages and disadvantages using batch reactors in bioprocessing.
1. 2. Decomposition of acetone dicarboxilic acid is a first order reaction :
1. 3. What sort of fermentation would not need to be performed in a fed batch manner?
Derive the mathematical expressions for various feeding mechanisms of fed batch reactor?
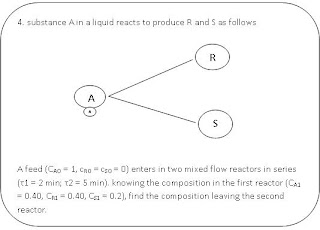
4. the below is the 4th question :
5. The following id the 5th Question :

ASSUME THAT the system is in an ideal solution :
f = yA fA, pure substance = yA π (fA, pure substance / π )
the quantity in brackets is given by the Newton charts, which may be found in most thermodynamics texts for chemical engineers.
1. 6. Behavior of short laminar flow reactors . Consider laminar flow in a tubular reactor, which is so short that the dispersion model is not applicable. For this situation prediction of behavior becomes very difficult, however we can still estimate the poorest expected performance of such reactors. As an example take a first order reaction A ---- R with XA, plug = 0.99. recalling for laminar flow that maximum velocity in the centerline of the pipe is twice the average velocity and that this represents the smallest residence time in the reactor estimate the lower bound to the expected conversion.
1. 7. Write about the stability analysis of bioreactors using mathematical model.
1. 8. Describe the mass transfer aspects you need to consider in the design of bioreactors.
SET : 2
1. What are the ideal flow conditions in a bioreactor? Explain them in detail.
2. What is meant by a homogenous reaction? What is its importance in fermentation industry? Explain in detail.
What is Michaelis – Menten equation? Describe its importance in enzymatic processor.
3. What is the difference between the specific growth rate (µ) and the rate of cell increase (dx/dt)?
Why do we use the specific growth rate to describe cell growth instead of the doubling time (or generation time)?
4. Reactant A decomposes in an isothermal batch reactor (CAO = 100) to produce wanted R and unwanted S and the following progressive concentration reading are recorded :
CA (100) 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 (0)
CR (0) 1 4 9 16 25 35 45 55 64 (71)
Additional runs show that adding R or S does not affect the distribution of products formed and that only A does. Also it is noted that the number of moles of A,R and S is constant.
a) Find the Ψ versus CA curve for this reaction. With a feed CAO = 100 and CAf = 10, find CR
b) From a mixed flow reactor
c) From a plug flow reactor
d) Repeat parts (b) and (c) with the modification that CAO = 70
5. For the system with CAO = 5 mol/lit
a) Find the space time in amixed reactor to achive 90% conversion of A to R
b) With a sketch show the location and determine the necessary heat exchanger if feed enters at 25 C, product leaves at 25 C, and the allowable temperature range is from 5 C to 95 C.
6. Describe how do you estimate the conversion in a bioreactor with nonideal flow behaviour using dispersion model.
7. Explain in detail the packed bed bioreactor dynamics using mathematical model?
8. Describe some characteristic features of a fermenter which are neede to be considered while designing a fermenter.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using off – centre impellers over baffles for creating turbellence? Explain in detail.
SET : 3
1. Derive the design equations for the following using mathematical models for :
a) CSTR
b) PFR.
2. Explain how do you calculate the first order reaction rate constant using various methods.
3. What is diauxie growth curve?
Why do cell numbers increase exponentially during the log phase in batch cultutre?
4. The desired liquid phase reaction :
A + B --------------- R + T , dCR/dt = dCT/dt = k1CA1.5CB0.30
Is accompanied by the undesired side reaction
A + B --------------- S + U , dCS/dt = dCU/dt = k2CA0.50CB1.8
What contacting schemes (reactor types) would you use to carry above reactions to minimize the concentration of the undesired products?
5. Determine the equilibrium conversion for the following elementary reaction between 0 C and 100 C.
6. The kinetics of a homogeneous liquid reaction are studied in a flow reactor, and to approximate plug flow the 48 cm long reactor is packed with 5mm nonporous pellets. If the conversion is 99% for a mean residence time of 1 sec calculate the rate constant for the first order reaction
a) Assuming that the liquid passes in plug flow through the reactor,
b) Accounting for the deviation of the actual flow from plug flow.
c) What is the error in calculated K if deviation from plug flow is not considered.
Data : Bed voidage = 0.4,
Particles Reynolds number = 200
7. Explain in detail the response of the nutristat operation?
8. Describe some characteristic features of a fermenter which are neede to be considered while designing a fermenter.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using off – centre impellers over baffles for creating turbulence? Explain in detail.
SET : 4
1. A gas mixture consisting of 50 mole% A and 50mole% inerts enter the reactor with the flow rate of 6l/s at 144C. the rate data is as follows :
XA 0 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.85
-rA 0.0053 0.0052 0.005 0.0045 0.004 0.0033 0.0025 0.0018 0.00125 0.001
If the reaction is carried out in two reactors in series with 40% conversion in the first reactor and 85% overall conversion, estimate the total volume of reactors when
a) Reactors are both mixed flow, and
b) Reactors are both plug flow.
2. A batch fermenter is being used for the production of yeast cells from glucose. The number of yeast cells is found to be in 1.5h. find the average specific growth of cells(µ).
3. What is the effect of mutation and contamination on the operation of a chemostat?
What are the problems associated with the culture of genetically engineered yeast in continuous culture system?
4. What are the various types of fermentation reactions? Explain with examples.
Explain in detail what are the effects of temperature, pressure, Ph on fermentation reactions.
5. Given the gas – phase reaction A = B + C. start with pure A. suppose that 50% of the original A is dissociated at 1000K and 10 atm as well as at 500 K and 0.1 atm.
a) Calculate the percent dissociation at 250 K and 1 atm
b) Calculate the % dissociation at 250 K and 0.1 atm.
Data : Average Cp of A = 12 cal/mol K
Average Cp of B = 7 cal/mol K
Average Cp of C = 5 cal/mol K
6. Define the following :
a) Dispersion coefficient
b) Dispersion number
c) Pecklet number
d) Damkohler number
7. How do you control the cascade bioreactors? Explain in detail using mathematical model.
8. Describe some characteristic features of a fermenter which are needed to be considered while designing a fermenter.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using off – centre impellers over baffles for creating turbulence? Explain in detail.


1 comments:
thanks a lot 4 keeping bre paper.i have been searching this 4 a long time.thanks a lot again
Post a Comment